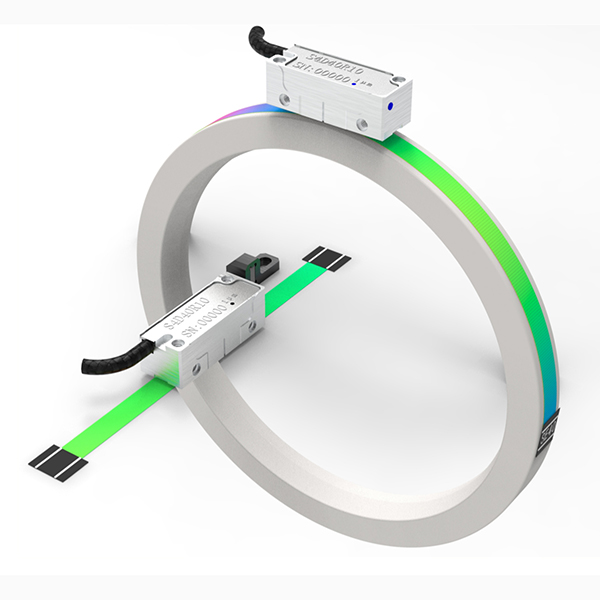
An encoder is a device that compiles and converts a signal (such as a bit stream) or data into a signal form that can be used for communication, transmission, and storage. The encoder converts angular displacement or linear displacement into an electrical signal, the former is called a code disc, and the latter is called a yardstick. According to the readout method, the encoder can be divided into two types: contact type and non-contact type; according to the working principle, the encoder can be divided into two types: incremental type and absolute type. The incremental encoder converts the displacement into a periodic electrical signal, and then converts the electrical signal into a counting pulse, and uses the number of pulses to represent the magnitude of the displacement. Each position of the absolute encoder corresponds to a certain digital code, so its indication is only related to the start and end positions of the measurement, but has nothing to do with the middle process of the measurement.
Classification of encoders
According to the detection principle, the encoder can be divided into optical type, magnetic type, inductive type and capacitive type. According to its calibration method and signal output form, it can be divided into three types: incremental type, absolute type and hybrid type.
Incremental encoder:
Incremental encoder directly uses the principle of photoelectric conversion to output three groups of square wave pulses A, B and Z phase; the phase difference between the two groups of pulses A and B is 90 degrees, so that the direction of rotation can be easily judged, while Phase Z is one pulse per revolution, which is used for reference point positioning. Its advantages are simple principle and structure, the average mechanical life can be more than tens of thousands of hours, strong anti-interference ability, high reliability, and suitable for long-distance transmission.
Absolute encoder:
Absolute encoder is a sensor that directly outputs numbers. On its circular code disc, there are several concentric code discs along the radial direction. The sector trees of the code track have a double relationship. The number of code tracks on the code disc is the number of digits of its binary number. On one side of the code disc is a light source, and on the other side there is a photosensitive element corresponding to each code track. When the code When the disk is in different positions, each photosensitive element converts a corresponding level signal according to whether it is illuminated or not, forming a binary number. The feature of this encoder is that no counter is needed, and a fixed digital code corresponding to the position can be read at any position of the rotating shaft.
Hybrid Absolute Encoder:
Hybrid absolute encoder, it outputs two sets of information, one set of information is used to detect the magnetic pole position, with absolute information function; the other set is exactly the same as the output information of the incremental encoder.
Post time: Feb-20-2023