JCX22 high-precision optical encoders
1. Product Overview
The steel belt grating is a precision measurement tool designed for linear and angular positioning applications in various industries. It combines robust construction with advanced optical technology for high precision and long-term reliability.
2. Key Features
High measurement accuracy with excellent repeatability.
Durable and resistant to harsh industrial environments.
Supports integration with automation and control systems.
Low-maintenance design for cost-effectiveness
3. Technical Specifications
Material: High-strength stainless steel.
Accuracy Grade: ±3 µm/m or ±5 µm/m (depending on model).
Maximum Length: Up to 50 meters (customizable based on requirements).
Width: 10 mm to 20 mm (specific models may vary).
Resolution: Compatible with high-precision optical sensors (up to 0.01 µm depending on system configuration).
Operating Temperature Range: -10°C to 50°C.
Storage Temperature Range: -20°C to 70°C.
Thermal Expansion Coefficient: 10.5 × 10⁻⁶ /°C.
Clock frequency: 20MHz
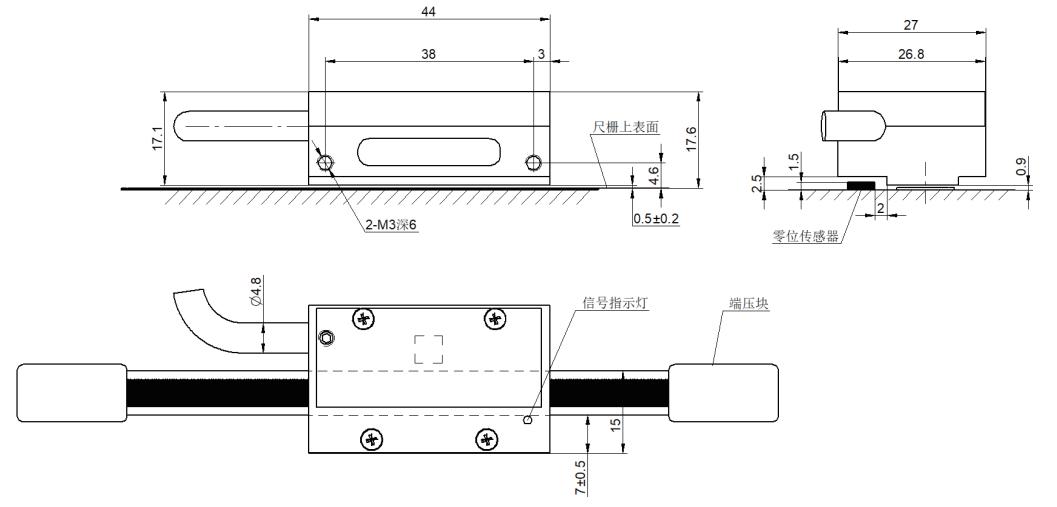
4. Dimension Drawing
The steel belt grating's dimensions are detailed in the technical drawing, which specifies the following:
Grating Body: Length varies based on model (up to 50 meters); width is between 10 mm and 20 mm.
Mounting Hole Positions: Precisely aligned for secure and stable installation.
Thickness: Typically 0.2 mm to 0.3 mm, depending on model.
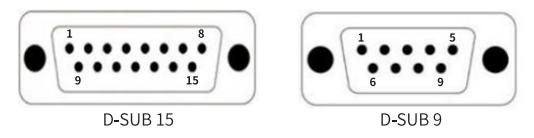
5. D-SUB Connector Details
Pin Configuration:
Pin 1: Power Supply (+5V)
Pin 2: Ground (GND)
Pin 3: Signal A
Pin 4: Signal B
Pin 5: Index Pulse (Z Signal)
Pin 6–9: Reserved for custom configurations.
Connector Type: 9-pin D-SUB, male or female depending on the system design.
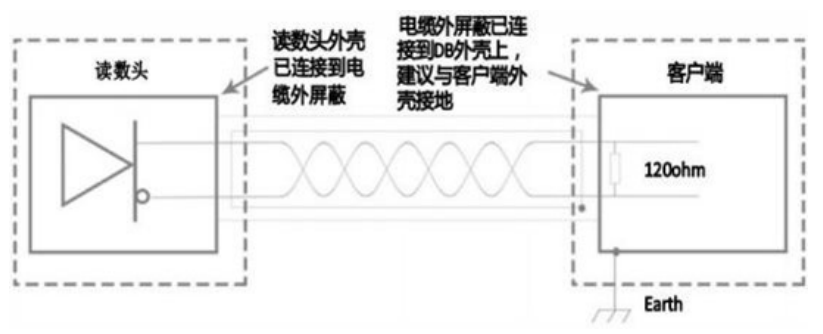
6. Electrical Wiring Diagram
The electrical wiring diagram outlines the connections between the steel belt grating and the system controller:
Power Supply: Connect the +5V and GND lines to a regulated power source.
Signal Lines: Signal A, Signal B, and Index Pulse should be connected to the corresponding inputs on the control unit.
Shielding: Ensure proper grounding of the cable shield to prevent electromagnetic interference.
7. Installation Guidelines
*Ensure the installation surface is clean, flat, and free of debris.
*Use the recommended mounting brackets and alignment tools for precise positioning.
*Align the grating with the measurement axis, ensuring no twists or bends.
*Avoid exposure to contaminants like oil or water during installation.
8. Operation Instructions
*Confirm proper alignment and calibration before use.
*Avoid applying excessive force to the grating during operation.
*Monitor for any deviation in readings and recalibrate as needed.
9. Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Maintenance:
*Clean the grating surface using a soft, lint-free cloth and alcohol-based cleaner.
*Periodically check for physical damage or misalignment.
*Tighten loose screws or replace worn-out components.
Troubleshooting:
*For inconsistent measurements, check alignment and recalibrate.
*Ensure optical sensors are free of obstructions or contamination.
*Contact technical support if problems persist.
10. Applications
The steel belt grating is commonly used in:
*CNC machining and automation.
*Robotic positioning systems.
*Precision metrology instruments.
*Industrial manufacturing processes.
Products categories
-

Phone
-
E-mail
-

Whatsapp
whatsapp

-

WeChat

-

Top